Class 6 Maths
Understanding Elementary Shapes


Question 1:
What is the angle name for half a revolution?
Question 2:
Through what angle measure does the hour hand of a clock turn through, when it goes from 3 to 9?
Question 3:
Which direction will you face if you start facing west and make 234 of a revolution anti – clockwise?
of a revolution anti – clockwise?
Question 4:
Identify the types of angles from the given figures:

Question 5:
What does the angle made by the hour hand of the clock look like when it moves from 5 to 7? Is the angle moved more than 1 right angle?
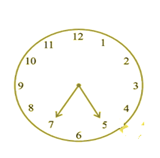
Question 6:
In the given figure, name the following angles as acute, obtuse, right, straight or reflex.
(a) ∠QOY
(b) ∠YOP
(c) ∠ROX
(d) ∠QOX
(e) ∠POQ
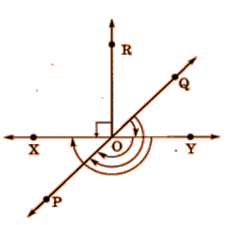
Question 7:
Fill in the blanks:
(a) A _________ is a rectangle with a pair of adjacent sides equal.
(b) A parallelogram with a pair of adjacent sides equal is called a _______.
(c) A quadrilateral having exactly one pair of parallel sides is called a __________.
(d) A quadrilateral having both pairs of opposite sides parallel, is called a _________.
(e) A parallelogram whose each angle is a right angle is called a _________.
Question 8:
Complete the given table for prisms:
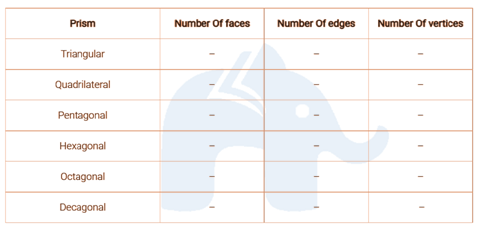
Question 9:
What fraction of a clockwise revolution does the hour hand of a clock turn through, when it goes from 12 to 3?
Question 10:
If A, B, C, are three points on a line such that AB = 5 cm, BC = 3 cm and AC = 8 cm, which one of them lies between the other two?
Question 11:
Find the number of right angles turned through by the hour hand of a clock when it goes from 4 to 10.
Question 12:
What are the types of the given triangles on the basis of angles?
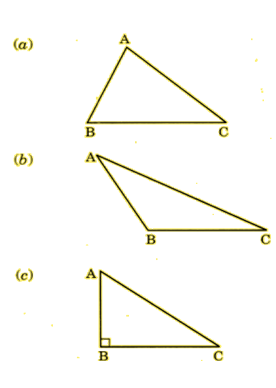
Question 13:
A bicycle wheel makes four and a half turns. Find the number of right angles through which it turns.
Question 14:
State the kind of angle, in each case, formed between the following directions:
(i) East and West
(ii) East and North
(iii) North and North-East
(iv) North and South-East
Question 15:
From the figure given below, write
(i) all pairs of parallel lines.
(ii) all pairs of intersecting lines.
(iii) lines whose point of intersection is I.
(iv) lines whose point of intersection is D.
(v) lines whose point of intersection is E.
(vi) lines whose point of intersection is A.
(vii) collinear points.
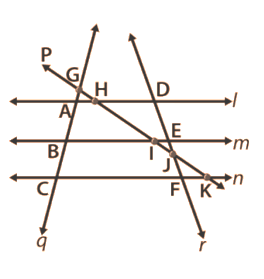
Question 16:
Fill in the blanks:
(i) A part of a line with two end-points is called a _______.
(ii) Segment AB is _____ segment BA.
(iii) The length of a line segment is the ________ distance between two end points.
Question 17:
Give two new examples of each of the following three dimensional shapes:
(i) Cone
(ii) Sphere
(iii) Cylinder
(iv) Cuboid
(v) Pyramid
Question 18:
Which of the following line-segments is longer?
Question 19.
Identify the parallel line segments shown in figure.
Question 20:
Give two examples each of:
(i) intersecting lines
(ii) parallel lines from your environment.
**********
In summary, problem-solving after learning a theoretical concept on CBSE Understanding Elementary Shapes Class 6 Maths is an essential part of the learning process. It enhances your understanding, critical thinking abilities, and retention of knowledge. Moreover, it equips you with valuable skills that are applicable in academic, personal, and professional contexts.
You must have heard of the phrase “Practice makes a man perfect”. Well, not just a man, practice indeed enhances perfection of every individual.
Practicing questions plays a pivotal role in achieving excellence in exams. Just as the adage goes, "Practice makes perfect," dedicating time to solve a diverse range of exam-related questions yields manifold benefits. Firstly, practicing questions allows students to familiarize themselves with the exam format and types of problems they might encounter. This familiarity instills confidence, reducing anxiety and improving performance on the actual exam day. Secondly, continuous practice sharpens problem-solving skills and enhances critical thinking, enabling students to approach complex problems with clarity and efficiency. Thirdly, it aids in identifying weak areas, allowing students to focus their efforts on improving specific topics. Moreover, practice aids in memory retention, as active engagement with the material reinforces learning. Regular practice also hones time management skills, ensuring that students can allocate appropriate time to each question during the exam. Overall, practicing questions not only boosts exam performance but also instills a deeper understanding of the subject matter, fostering a holistic and effective learning experience.
All About Daily Practice Problems on Class 6 Maths Understanding Elementary Shapes NCERT Chapter 5
Our Daily Practice Problems (DPPs) offer a diverse range of question types, including Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) as well as short and long answer types. These questions are categorized into Easy, Moderate, and Difficult levels, allowing students to gradually progress and challenge themselves accordingly. Additionally, comprehensive solutions are provided for each question, available for download in PDF format - Download pdf solutions as well as Download pdf Questions. This approach fosters a holistic learning experience, catering to different learning styles, promoting self-assessment, and improving problem-solving skills. With our well-structured DPPs, students can excel in exams while gaining a deeper understanding of the subject matter. Hope you found the content on Class 6 Maths Understanding Elementary Shapes NCERT Chapter 5 useful.
Last but not least, to get the best hold on Class 6 Maths Understanding Elementary Shapes NCERT Chapter 5, do not forget to check out: