Class 7 Maths
Data Handling


Question 1:
Ashish studies for 4 hours, 5 hours and 3 hours respectively on three consecutive days. How many hours does he study daily on an average?
Question 2:
The ages in years of 10 teachers of a school are:
32, 41, 28, 54, 35, 26, 23, 33, 38, 40
(i) What is the age of the oldest teacher and that of the youngest teacher?
(ii) What is the range of the ages of the teachers?
(iii) What is the mean age of these teachers?
Question 3:
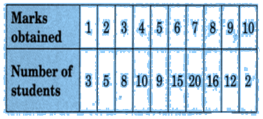
The marks obtained (out of 10) by 80 students in a class test are given below:
Find the mode of the above data.
Question 4:
A bag contains 8 white and 12 red balls. One ball is drawn at random from the bag. Find the probability of getting
(a) a white ball
(b) a red ball
Question 5:
The data given below shows the production of motorbikes in a factory for some months of two consecutive years.
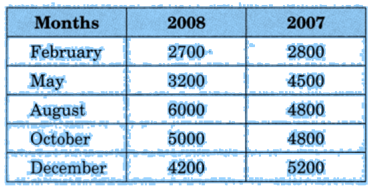
Study the table given above and the answer the following questions:
(a) Draw a double bar graph using an appropriate scale to depict the above information and compare them.
(b) In which year was the total output maximum?
(c) Find the mean production for the year 2007.
(d) For which month was the difference between the production for the two years is the maximum?
(e) In which month for the year 2008, the production was the maximum?
(f) In which month for the year 2007, the production was the least?
Question 6:
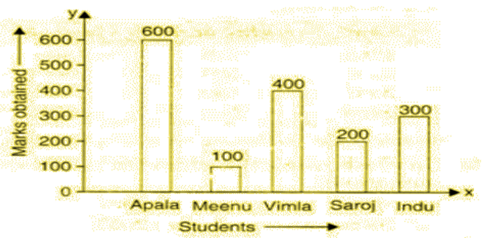
Read the following bar graph and answer the following related questions:
(a) Who got the maximum marks?
(b) Who got the minimum marks?
(c) What is the difference between maximum and minimum marks?
(d) What is the ratio between the marks obtained by Saroj and Vimla?
(e) How many girls have got marks more than 100?
(f) The difference between the marks obtained by Vimla and Saroj is how many times the difference between the marks obtained by Meenu and Saroj?
Question 7:
Find the median of the following data:
20, 14, 6, 25, 18, 13, 19, 10, 9, 12
Question 8:
A coin is tossed. What is the probability of getting tail?
Question 9:
Following are the margins of victory in the football matches of a league.
1, 3, 2, 5, 1, 4, 6, 2, 5, 2, 2, 2, 4, 1, 2, 3, 1, 1, 2, 3, 2,
6, 4, 3, 2, 1, 1, 4, 2, 1, 5, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2, 4, 2, 1, 2
Find the mode of this data.
Question 10:
Which of the following statements is true?
(a) The mode is always one of the numbers in a data
(b) The mean is always one of the numbers in a data
(c) Mean < Mode in a data
(d) Median < Mode in a data
Question 11:
Which of the following is the mean of the given data?
(a) The middle value of the data arranged in ascending or descending order.
(b) The value of the observation occurring most frequently.
(c) The sum of all the values of the data divided by the total number of values.
(d) None of these.
Question 12:
Fill in the blanks:
(a) The difference between the highest and the lowest observation is called the ………………… of the data.
(b) The observation occurring the most in a set of given data is called the ………………… of the data.
(c) The mean of the first five natural numbers is ………………….
Question 13:
The bar graph shows the result of a survey to test water resistant watches
made by different companies. Each of these companies claimed that their watches were water resistant. After a test the above results were revealed.

(a) Can you work out a fraction of the number of watches that leaked to the number tested for each company?
(b) Could you tell on this basis which company has better watches?
Question 14:
A die is rolled. Find the probability that the number of dot’s on its upper face is less than 5.
Question 15:
A coin and a die are tossed once together. Find the total number of outcomes.
Question 16:
If the averages of the given data 6, 10, 12, x, 16 is 14, find the value of x.
Question 17:
Find the mean of the first 6 multiples of 3.
Question 18:
The rainfall (in mm) in a city on 7 days of a certain week was recorded as follows:
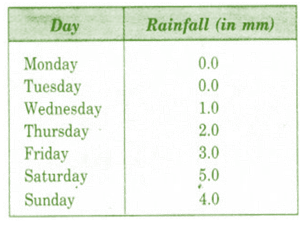
On how many days was the rainfall less than 6 mm?
Question 19:
The number of tourists visiting a historical place in a week is shown in the following table:
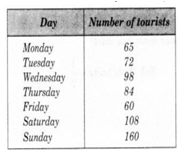
(a) On which day 60 tourists visit?
(b) What is the difference between the number of tourists visiting on Friday and Monday?
(c) What is the difference between the maximum and minimum number of tourists?
Question 20:
The marks of 11 students of a class are as given below:
78, 11, 99, 63, 94, 6, 78, 36, 30, 55, 22
Find the range of marks.
*********
In summary, problem-solving after learning a theoretical concept on CBSE Data Handling Class 7 Maths is an essential part of the learning process. It enhances your understanding, critical thinking abilities, and retention of knowledge. Moreover, it equips you with valuable skills that are applicable in academic, personal, and professional contexts.
You must have heard of the phrase “Practice makes a man perfect”. Well, not just a man, practice indeed enhances perfection of every individual.
Practicing questions plays a pivotal role in achieving excellence in exams. Just as the adage goes, "Practice makes perfect," dedicating time to solve a diverse range of exam-related questions yields manifold benefits. Firstly, practicing questions allows students to familiarize themselves with the exam format and types of problems they might encounter. This familiarity instills confidence, reducing anxiety and improving performance on the actual exam day. Secondly, continuous practice sharpens problem-solving skills and enhances critical thinking, enabling students to approach complex problems with clarity and efficiency. Thirdly, it aids in identifying weak areas, allowing students to focus their efforts on improving specific topics. Moreover, practice aids in memory retention, as active engagement with the material reinforces learning. Regular practice also hones time management skills, ensuring that students can allocate appropriate time to each question during the exam. Overall, practicing questions not only boosts exam performance but also instills a deeper understanding of the subject matter, fostering a holistic and effective learning experience.
All About Daily Practice Problems on Class 7 Maths Data Handling NCERT Chapter 3
Our Daily Practice Problems (DPPs) offer a diverse range of question types, including Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) as well as short and long answer types. These questions are categorized into Easy, Moderate, and Difficult levels, allowing students to gradually progress and challenge themselves accordingly. Additionally, comprehensive solutions are provided for each question, available for download in PDF format - Download pdf solutions as well as Download pdf Questions. This approach fosters a holistic learning experience, catering to different learning styles, promoting self-assessment, and improving problem-solving skills. With our well-structured DPPs, students can excel in exams while gaining a deeper understanding of the subject matter. Hope you found the content on Class 7 Maths Data Handling NCERT Chapter 3 useful.
Last but not least, to get the best hold on Class 7 Maths Data Handling NCERT Chapter 3, do not forget to check out: